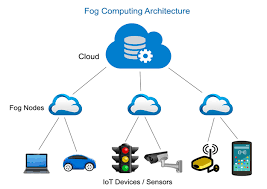
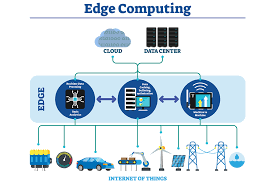
Our Fog-Edge Approach
Fog Computing serves as an intelligent intermediate layer between edge devices and the cloud. By processing data closer to the source (e.g., gateways or local servers), it ensures:
- Coordinated decision-making across distributed nodes
- Low-latency communication for time-critical applications
- Reduced bandwidth usage and less dependency on the cloud
Example: Fog nodes deployed across a city synchronize edge sensors from multiple streets, optimizing traffic flow on a citywide scale.